The specification of 66 kV wire and cable with xlpe insulation makes it usable in underwater conditions. XLPE cables are insulated with XLPE, a material that is gaining popularity due to its distinct physical and chemical properties.
These cables have good qualities that make them suitable for various applications in any environment due to the cruciform structure of the polyethylene molecules that make up the cables.
For example, these cables are capable of handling voltage classes from 600 V to 130 kV. As a result, they produce XLPE cables in high, medium and low voltage varieties.
In the following paragraphs, we will explore this type of cable and discover how to use XLPE cables to connect your electrical equipment to get the maximum power.
A cable that has an insulation or sheath made of cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) is called an XLPE cable.
The coating that is wrapped around the conductors inside the cable is called insulation. However, the sheath is the most protective layer for the cable, and both the sheath and the cable itself must be able to prevent the flow of electricity.
The insulation material for these cables is often made of cross-linked polyethylene, which has a molecular dielectric structure that is cross-polarized rather than linearly polarized.
These cables are usually used in high voltage applications. The word XLPE may be divided into two parts: the first two letters indicate the same structure, while the last two letters indicate polyethylene.
Due to the ionic cross structure, the cable is more flexible and resistant to mechanical stress, moisture, corrosion and heat. Also, resistance to these factors has increased.
Ducting in buildings with high relative humidity is one of the most common applications of XLPE cables.
The following elements make up this particular variety of cable:
Conductor: The term “conductor” refers to the central core of the cable, which is responsible for the transmission of electric current.
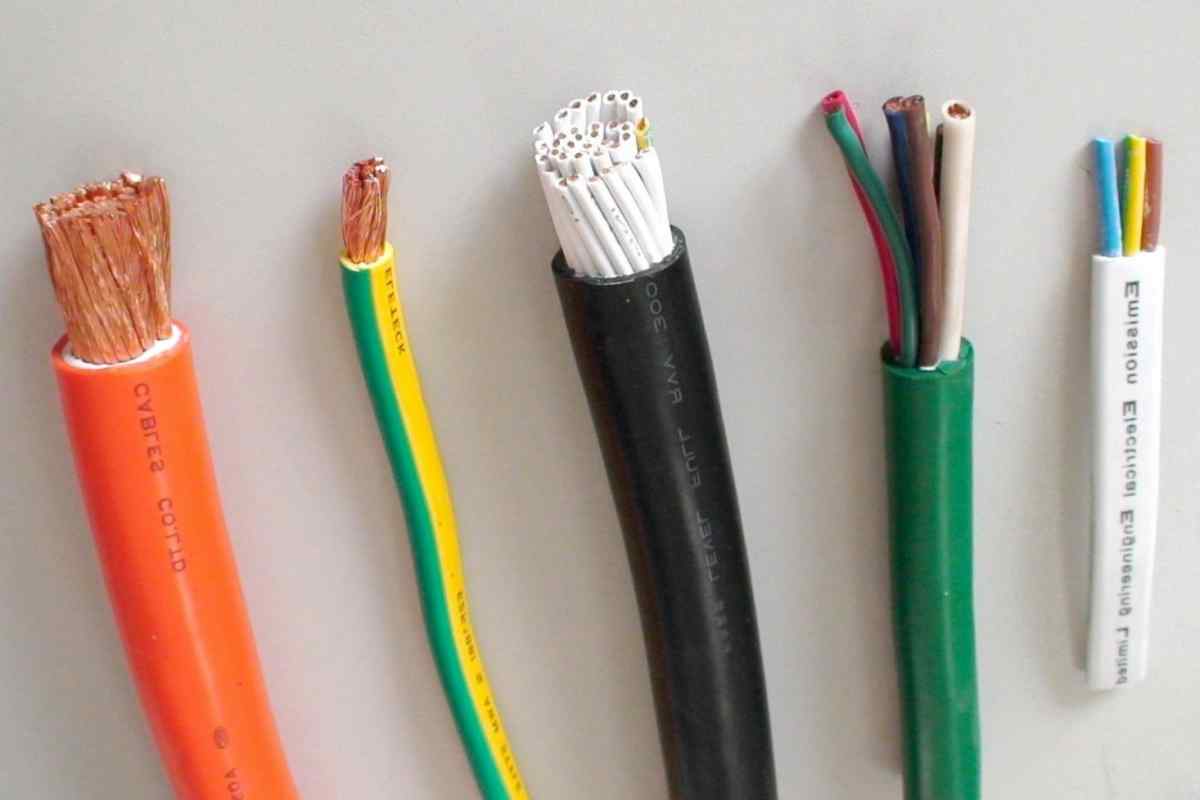
Both copper and aluminum are examples of common materials used in the production of conductors. The voltage of 600 volts is suitable for this type of cable.
Semiconductor layers: These layers, also called “semiconductor layers”, are used to neutralize and distribute the electric field uniformly.
Insulation: There is a layer of insulation around the conductor to prevent current leakage into the cable. The insulation in this type of cable is made of XLPE material.
The term filler refers to the material that is inside the cable and is responsible for filling the spaces between the internal insulation, the conductors and the outer sheath.
Outer sheath or jacket: PVC is the outermost part of the cable. It is responsible for insulating the cable and preventing current leakage that may occur if the internal insulation is torn.
Copper conductors are placed between layers of XLPE thermoset insulation in the cable, which is labeled USE-2, which stands for Underground Service Entry.
Since thermostats can withstand a certain amount of tolerance, these cables can be used in underground applications such as buried cables. As a result of the tolerance of the thermostat, they show good resistance against thermal and mechanical stresses.
On the other hand, due to the high resistance of the cable against heat, humidity and sunlight, it is suitable for use in industrial applications such as the power supply of production machines. The voltage of 600 volts is suitable for this type of cable.
RHW-2: The letters “R”, “H” and “W” in the name of this insulator stand for XLPE body rubber insulators, which are resistant to temperatures above 75 degrees Celsius and water penetration.
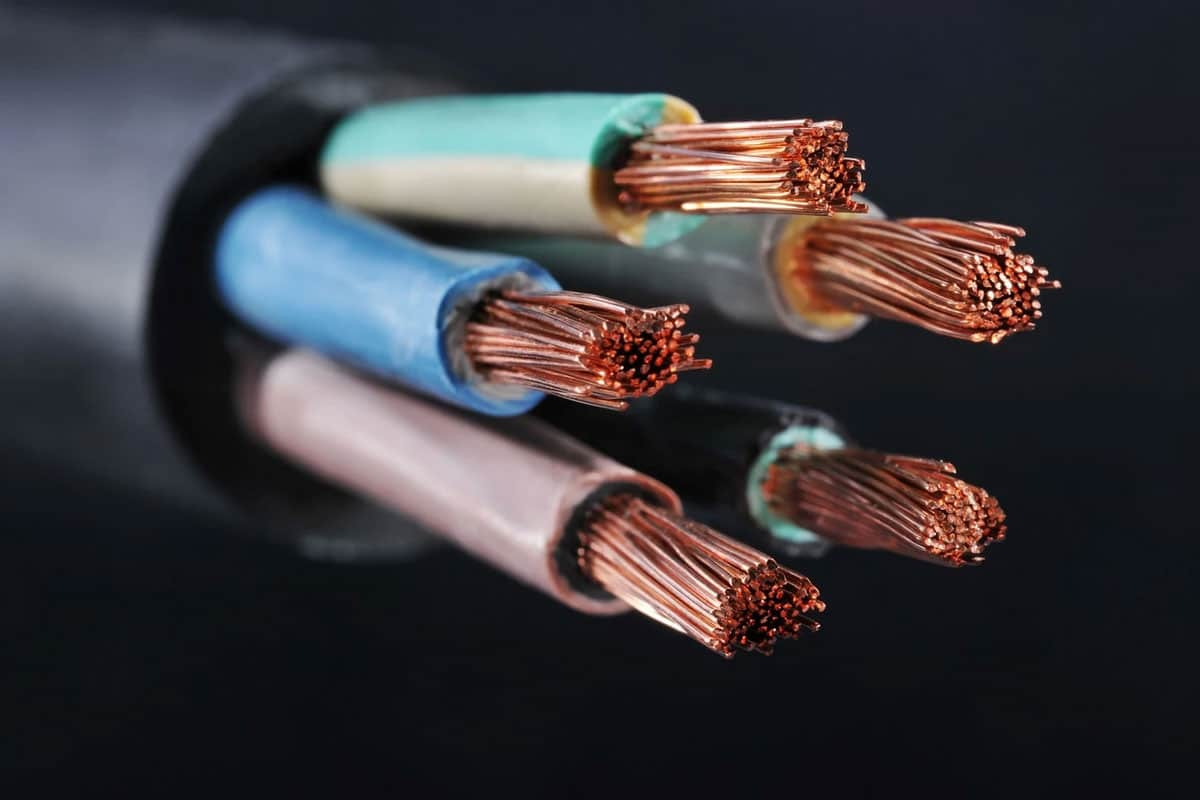
This insulation is also known as RHW-2. The rubber or neoprene used to make this cross-linked polyethylene gives it high resistance to moisture.
The fact that these cables have the number 2 in their name indicates that they can withstand temperatures of 90 degrees Celsius.
The same is true for USE-2 cables. This cable can be buried in dry or wet soil, depending on how well it can handle either of those conditions.
This type of XLPE cable has a voltage of 600 volts and is suitable for use in electrical systems as well as ordinary wiring.
RHH: The first letter of the name of this cable, which is used to define the material it is made of, is “rubber insulation”. Similar to the previous two types, this model is an XLPE cable that operates at low voltage and supports voltages up to 600V.
It has good heat resistance at temperatures above 90 degrees. Although there are two h’s in a row in the model name, this cable is not waterproof.
However, high temperature resistance is indicated by those letters. These types of cables like RHW-2 are used for power transmission in production facilities as well as electrical facilities.
In addition, these cables are used for general purposes such as switchboards. However, environmental factors must also be considered.
There are two main differences between XLPE cables and other types of cables that allow you to identify them. However, other performance characteristics, such as heat resistance up to 90 degrees, may indicate that the cable in question is of the XLPE type.

These two goals are as follows:
compatibility of cable insulation coating inside;
Unlike PVC cables, which are generally black in color, XLPE cables are usually in shades of white, gray, and sometimes black.
When should XLPE cables be used and why should they be used?
Under the following conditions, XLPE cables may be used in industrial settings:
Temperature conditions that are either too cold or too hot.
Electrical applications that require high voltage.
exposed to wear and tear caused by mechanical tension;
areas that are wet or under water;
Places that are exposed to various pollution.
Some of the advantages of XLPE cables are as follows:
Due to the quality of XLPE, it has a higher resistance to heat and reaches up to 90 degrees Celsius.
Due to the cross-linked polyethylene structure of the cable, its flexibility and capacity to change its shape are inherent features.
Resistant to solvents and able to maintain its original electrical properties even when exposed to chemicals.
It has the ability to withstand an increase in temperature up to 250 degrees Celsius for a limited period of time.
In addition, this type of cable is highly resistant to moisture and mechanical stress as well as to the effects of sunlight.
In the following material, we have collected some special advantages of 66 kV cable:
High continuous current rating: 90°C continuous operating temperature enables XLPE cables to carry higher amperage than PVC or paper insulated cables.
Small deformation at high temperature: Under a combination of thermal and mechanical stress, XLPE has little deformation compared to other solid dielectrics.
High Short Circuit Value: XLPE insulated cables have a maximum allowable continuous temperature of 250°C during short circuit, which greatly increases the short circuit value of XLPE cables compared to PVC and paper insulated cables.
Low dielectric loss: The dielectric loss of XLPE is much lower than traditional solid dielectrics such as PVC and EPR. This cost savings is huge when higher voltage power transmission is done over XLPE cables.
High emergency overload capacity: XLPE cables can operate up to 130°C in emergency conditions. This should not exceed 100 hours in a continuous 12 month period and 500 hours over the life of the cable.
Low charging current: The charging current is much less than other dielectrics. This activates the protective relay closing assembly.
wires and cables with our product pricing policy in line with global market prices.
You can easily contact us and be sure that you will get a relatively lower price than the market. So fill out the application form, let us know what you need and we’ll get back to you right away.









Your comment submitted.