The Internet is moving towards providing a platform for technologies and things to be connected. To provide the infrastructure of the so-called Internet of Things, 5G Internet is compared against optical fiber or optical fiber.
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolution has arrived. In the coming years, we will have billions of devices feeding us a constant stream of data, which in turn will revolutionize other areas.
Who provides broadband access to the vast army of IoT devices scattered across a wide range of IT estates is a topic of much interest.
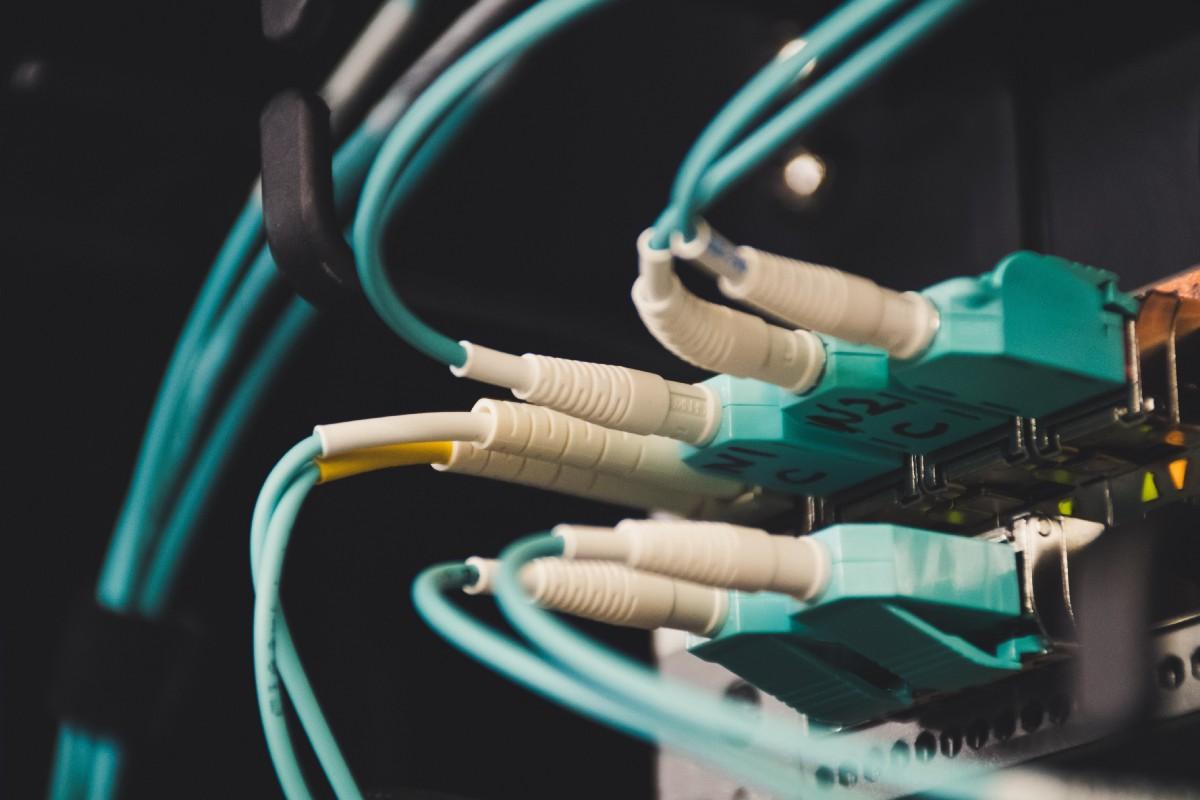

5G or fiber optic – which one will it be? Don’t simply assume that everyone will immediately gravitate to 5G for their IoT environment, based on the fact that there is so much hype surrounding the new technology known as 5G, it tends to take up a lot of the room’s oxygen.
Although 5G is suitable for the needs of the Internet of Things (IoT), it is not suitable for all situations.
As a result of the fact that both the 5G market and the fiber optic market are expected to grow significantly (at a compound growth rate of more than 20%) in the next five years, both of these data transmission technologies will play an important role. . In the future that is to come.
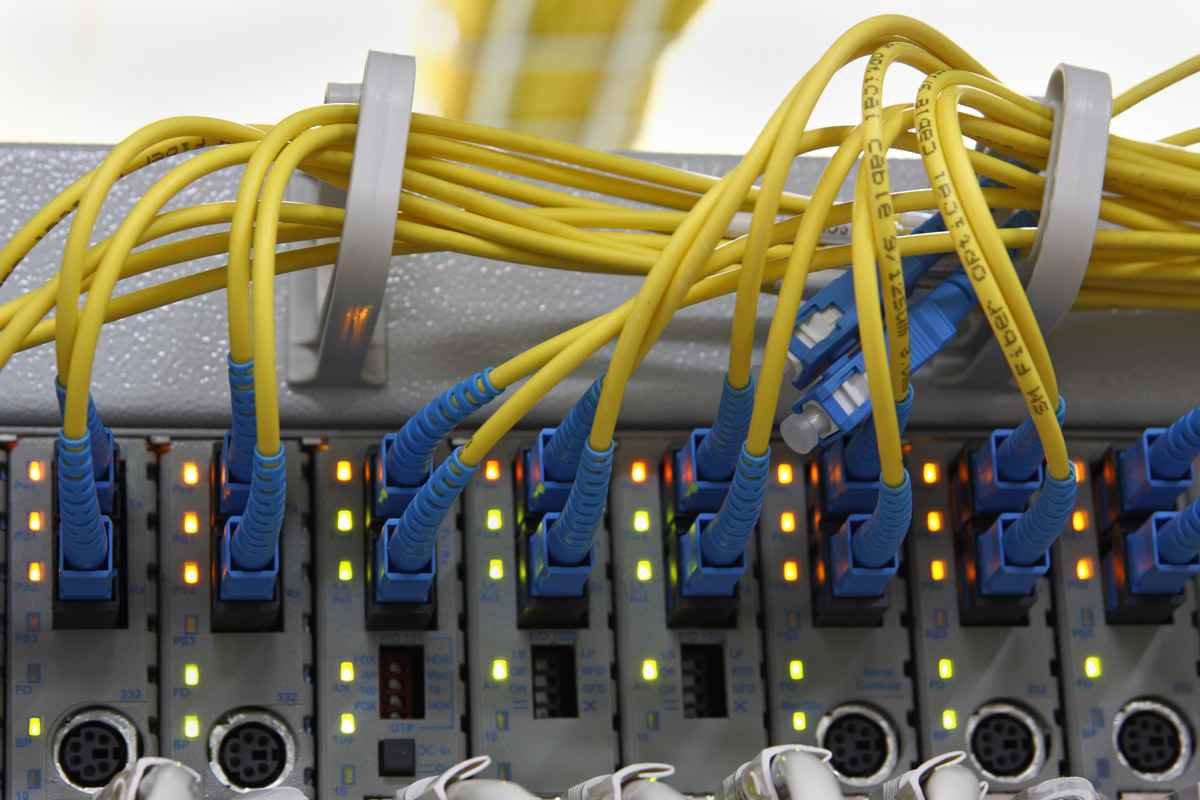
Key differences between 5G and fiber optics The transmission techniques used by fiber optics and 5G are completely different from each other.
Because 5G sends and receives data over radio waves, its coverage has a unique quality that sets it apart from 4G.
To communicate with the outside world, IoT devices only need to be located in an area served by 5G towers.
On the other hand, data can be sent through a fiber optic cable using light that travels through glass strands enclosed in the cable.
To take advantage of the direct point-to-point connectivity of fiber optics, IoT devices must somehow connect to the fiber itself.
Prices and construction organizational systems are also very diverse. It doesn’t matter what kind of cable it is. Cable routing is inconvenient, and laying fiber optic cable across an entire urban area is no easy task.
Underground conduits must be used to feed fiber to the network. Last mile installation for 5G is not only significantly more expensive, but also takes significantly longer to deploy.
The deployment of 5G networks is significantly less disruptive due to the fact that radio waves travel through the air.
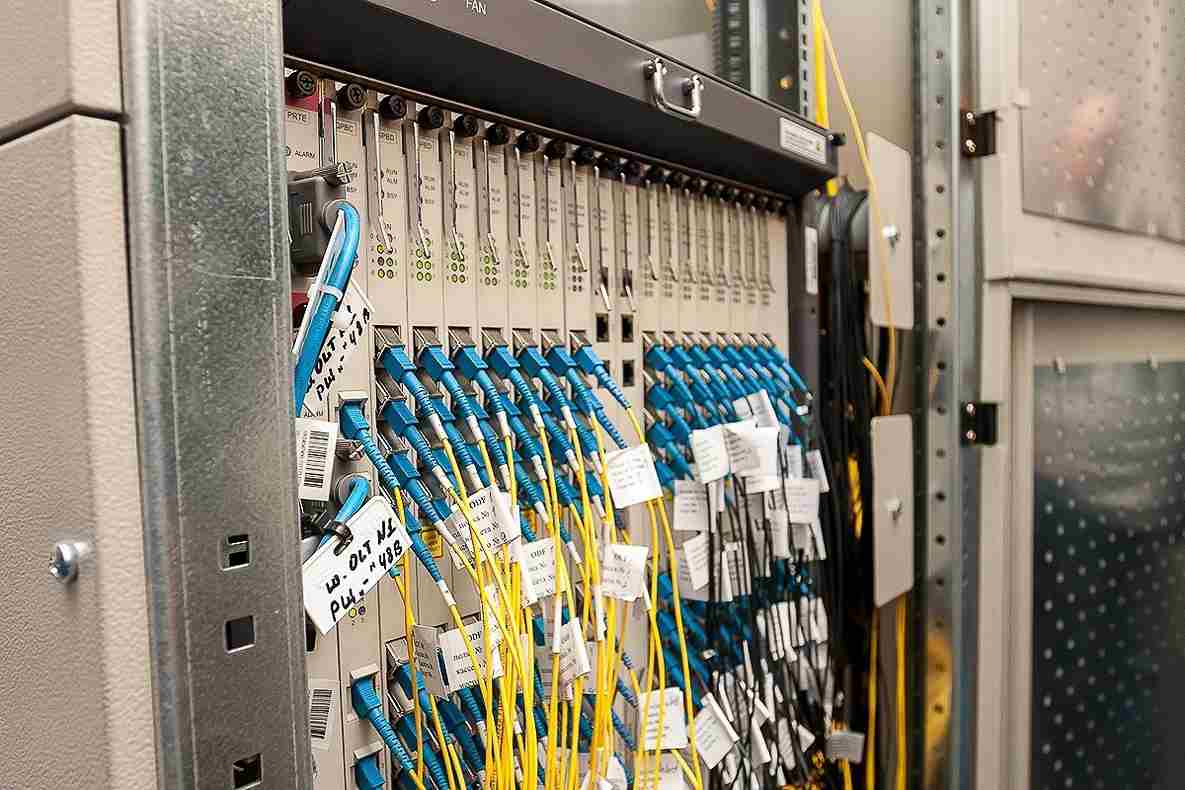

This allows the roll movements to occur faster and at a lower cost. In terms of installation costs, 5G is placed at the top, but the cost of doing it is significantly higher than in other networks. However, a fiber piece needs very little maintenance over its lifetime. Finally, 5G achieves user victory compared to other technologies in real cost. So there’s a long way off. The range of radio waves used by 5G is about 100 meters, significantly smaller than 4G. As a result, 5G is dependent on a network of towers and antennas, which is significantly smaller than that used by 4G before it. So, if you need to transmit data at a very large distance, you need a very large number of towers. Data may be transmitted over 70 kilometers using fiber optic cables without experiencing any damages. Optical fibers due to their ability to transmit data through large rural areas with relatively low binding density is a significant solution. Energy efficiency is the last factor of the distinction. When compared to a cellular tower, the amount of energy required to operate a fiber piece is much lower. This may not seem like a big problem, but this is what needs to be considered when business is promoting green performance and efficiency. The relationship between 5G and optical fiber, although the fiber-optic cable is much faster than 5G at this time, 5G-back technology is still at its beginning and will continue to improve. While 5G has a potential speed of 20 Gbps, the fiber optic can achieve speeds of up to or even over 100 Gbps. Despite the fact that those speeds are purely theoretical, the fiber rises no matter how you look at them. Both technologies are known for having a great response time; However, optical fibers function somewhat better with lower latency rates.
So where the use of optical fibers is more convenient, despite all the hoopla around 5G, there are still several scenarios where the choice for optical fiber is superior: 1. When it comes to safety and protection, optical fibers have always had a good reputation. Since it is impossible to access any single fiber glass filament in fiber optic cables, this technology is a clear choice to protect the Internet from the data of things that are transmitted through regional networks. 2. Delay problem is one of the issues that have been and will be problematic for cellular technology. When low latency performance is of great importance, there is no choice but to rely on the optic’s fast-power reaction. 3. As mentioned earlier, the fiber is superior in terms of long-distance transmission. Fiber optics is certainly a superior choice about transferring flow from sensory data to a centralized location from a remote weather station. It was not reasonable to think that there could be any of the country’s submersible, with 5G towers and antennas everywhere. 4. Although 5G has a significant presence in cities today, challenges that come with the surrounding urban environment should not be underestimated. This is due to the fact that the 5G signal cannot easily pass through physical barriers or dense vegetation. Fiber may be a preferred option in extremely crowded areas, although fiber installation may cost much more than in running cables. Where 5G makes more sense to leave the question, will 5G be the best choice for the Internet of things environments? Simply put, the answer to this question is a straightforward Yes. Initially, there are some settings where the fiber optic cable installation is not possible for various reasons. This goes beyond the problem set by the environment and the topography.

When it comes to high capacity and mobility status, 5G is no competition, despite the fact that this may not be the fastest or most reactive technology available. 5G is difficult in cases where a large number of sensing devices gather together and require data to be transferred somewhere. There’s nothing that can be physically connected to. There is no need to purchase or install any intermediate equipment such as switches. The simplicity and convenience of Wi-Fi are provided by 5G, but with increasing speed and responsiveness. A huge factory that relies on hundreds of sensory systems traveling down the production line is a famous picture of this environment. Another example would be a large army of high-definition video cameras that work together. Coverage of all frequencies used by 5G networks is required for automated vehicles. Working together rather than competing together is a shared thing. Although it is often fun to compare two different technologies with each other, you have to actually think about how those technologies can complement and strengthen each other. This is because 5G relies on optical fiber technology. At some point, these towers rely on fiber-optic connectors to get their data to the next high-density location, despite the fact that many large areas of the city have high-density areas of 5G coverage.

Electrical Wire Brands
There are many brand name companies that produce and sell electrical wires in the market, such as Sumitomo Electric Bunch which may be a global organization consisting of 415 companies in 40 countries.
The organization began in 1897, when our parent company Sumitomo Electric Industries was founded in Osaka, Japan.
The main activity of this company is the production of copper wire for cable.
Since then, we have diversified into five core business segments: Automotive, Infocomm, Electronics, Environment & Energy, and Industrial Materials.
Today, the Sumitomo Electric Group has more than 280,000 employees worldwide.
LEONI’s largest customer base includes the global automotive, commercial vehicle and parts supply industries, where the company manufactures standard and specialty cables as well as custom wiring systems and related components.
LEONI also provides products and services for the following markets: communications and data networks, healthcare, process industries, transportation, energy and infrastructure, factory automation, machinery and sensors, and marine.
Kabul Square Square is a strong partner for customers.
This company was established in 1978 and is known for producing quality wire and cable in the market.
The company has a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in Badi, Himachal Pradesh.
Indian Cable Company In 1957, two businessmen founded two German companies, Siemens and F&G, which manufactured various types of cables.
The company has now become a leading manufacturer of PVC insulated and sheathed cables, wires and cables. Howls of India Few people have not heard the name “Howls”.
This company produces kitchen appliances, water heaters, wires and cables, capacitors, personal cleaning supplies, air conditioners, water purifiers, etc.
The company was established in 1971 in Noida. The company has a turnover of around Rs 7,000 crore and operates in India and abroad.
It also has production sites in Europe, Africa, China and Latin America.
V-Guard Industries Ltd. Based in Cochin, Kerala, Way Guard manufactures power cables, voltage regulators, electric pumps, geysers, electric fans, electric motors and more.
Way Guard is one of the oldest companies in this field. It is spread across India with the help of more than 20,000 retailers and 500 distributors.
These two transmission methods will be combined for the foreseeable future, at least until 5G becomes significantly more widespread.

We offer a wide range of wires and cables with our product pricing policy in line with global market prices. You can easily contact us and be sure that you will get a relatively lower price than the market.
So, fill out the application form, let us know what you need and we’ll get back to you in no time.









Your comment submitted.